Understanding DC Motors: Beginner’s Overview
Taking a Look at How Electrical Energy Performs Work
Motors are devices that transform electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling machines and tools to perform useful work. One type of motor is the DC motor, which runs on direct current (DC) electricity.
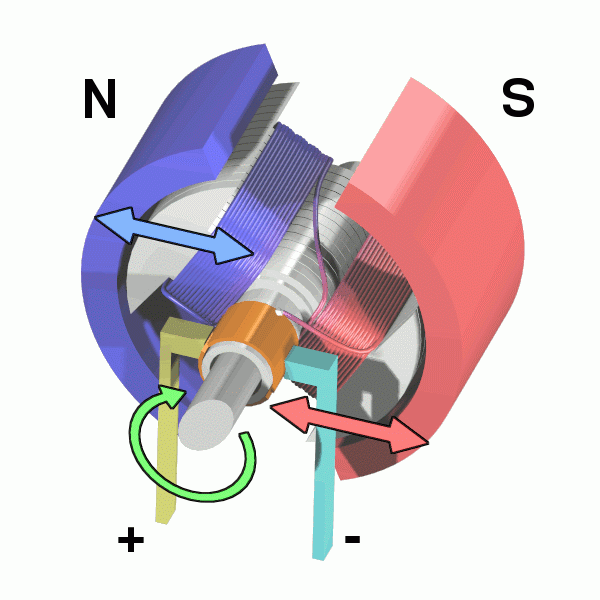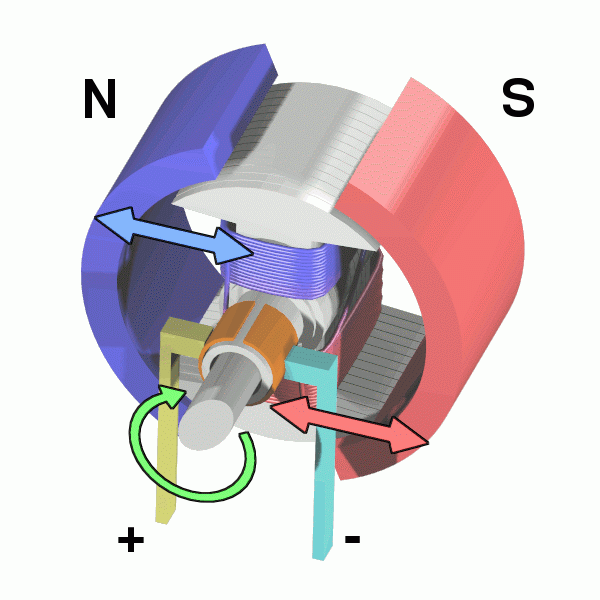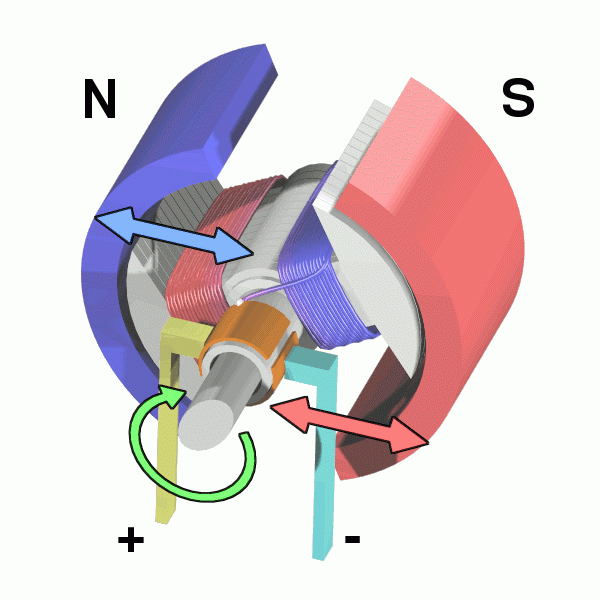
Why DC Motors When Buildings Use AC Power?
DC motors are used in applications requiring control over speed and torque, such as robotics, electric vehicles, conveyor belts, small household appliances, and construction power tools. While buildings are generally powered by AC electricity due to its efficient transmission over long distances, DC motors are preferred for tasks that require steady, adjustable speed. In many cases, an AC-to-DC converter called a “rectifier” is used to adapt the power supply.
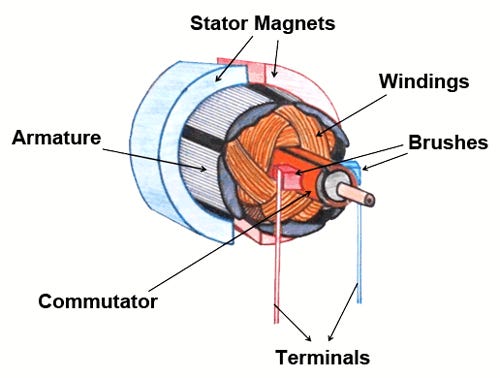
Basic Components of a DC Motor
A DC motor consists of several components, each playing a role in turning electrical energy into mechanical motion:
Terminals – This is where the electrical power enters the motor, providing the energy needed for operation.
Brush Arms & Brushes – These conduct electricity to the rotating parts of the motor.
Commutator – These act like a switch, directing of current flow into the coils to keep the motor spinning.
Coils – Wound wire coils create a magnetic field when electricity flows through them, driving the motor’s rotation.
Rotor & Armature – These are the spinning parts of the motor. The armature is the core structure that holds the coils and rotates under the influence of the magnetic field.
Stator – The stationary part of the motor that holds the magnets or windings, creating the necessary electromagnetic forces.
Permanent Magnets – Provide a stable magnetic field that interacts with the coils to produce motion.
Shaft – The rotating component that transmits mechanical energy to the machine or device being powered.
DC motors are everywhere, quietly powering the technology we rely on daily.⚡The YouTube channel The Engineering Mindset does a fantastic job explaining the workings of a DC motor.

